Week 3
In this week, I moved on to more basic python concepts and functions
Python Data Types
There are a multitude of data types in python. Some main types are: String, Integer and Float.
In python different data types do different things. And can be assigned using the class like:
print(int(80))
If a data type is not specified, it is assigned by default - which works for most cases.
Logical Conditions (if, elif, else)
If statements compare two variables and validate whether the output is true or false.
The "elif" statement is essentially - else, if.
This means if the previous statement was false, compare this. For example:
if b > a:
print("b is greater than a")
elif a == b:
print("a and b are equal")
else:
print("a is greater than b")
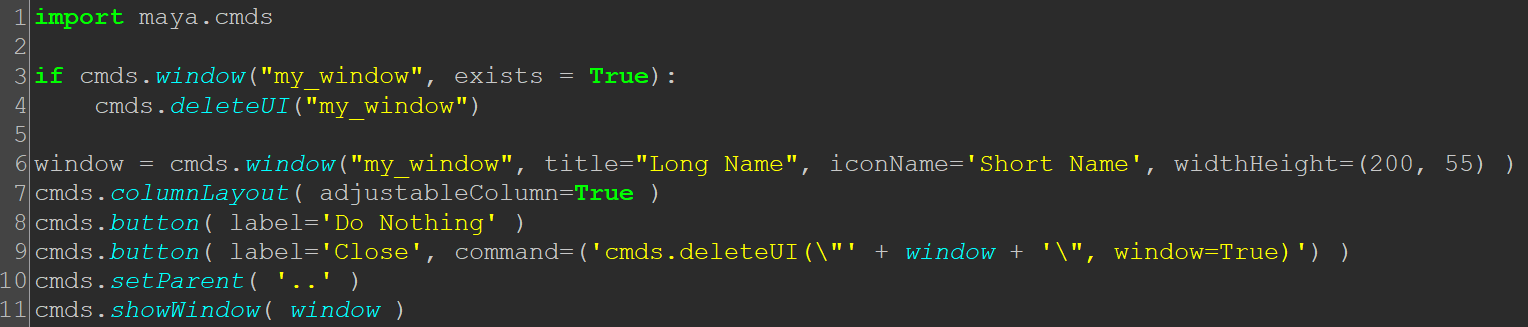
Maya Window Manipulation
In this example I explore the documentation for the window() command and create an if statement.
Collections (arrays)
Collections are a way of storing sets of information; improving the efficiency of inputting, outputting and processing data.
Some examples of collection data types are: Dictionaries, Tuples, and Lists.
Loops
Loops allow a section of code to be repeated until a certain condition is met.
A while loop is one type of loop that will repeat until a condition is met.
A for loop will repeat until a certain count is reached.
Week 3 Activities
1) Making Decisions
number = int(input("Please input a number: "))
if number == 12:
print("Your number is: "+ str(number))
elif number < 12:
print("Your number (" + str(number) + ") is lower than 12")
else:
print("Your number (" + str(number) + ") is greater than 12")
Output: 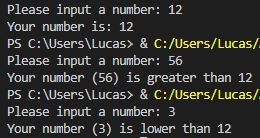
2) More Decisions
By changing all the occurances of the number in the code above, I can change the output to a different number e.g. 7.
Output : 
Smallest number Program
num_1 = int(input("Please input a number: "))
num_2 = int(input("Please input another number: "))
numbers = [num_1, num_2]
numbers.sort()
print("The smallest number is: " + str(numbers[0]))
Here I make use of python lists to get the smallest number. This can be done many ways but the advantage of this method is that I can easily add new user inputs to the array and always get the smallest number.
Output: 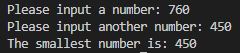
3) More Python Conditionals
y = int(input("Enter a number between 1 and 10: "))
if y == 1:
print("y is 1")
if y > 5:
print("y is high")
if y < 5:
print("y is low")
if y != 7:
print("y is unlucky")
if y == 2 or y == 3:
print("y is 2 or 3")
if y > 4 and y <= 7:
print("y is mid-range")
8) Loops
for i in range(6):
print("Python is awesome!")
9) More Loops
days = ["Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday"]
weekday = 1
for day in days:
print(day + " is day " + str(weekday) + " of the week")
weekday = weekday + 1
Output: 
10) Work Out This!
In this task, I modified the code by adding a condition to the start of the for loop. This checks the number and adds the corresponding suffix (st, nd, rd, etc.). Since all dates after 3rd use the "th" suffix, I could use an else statement as all the numbers with unique suffixes would be filtered out by the previous conditions.
days = ["Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday"]
weekday = 1
for day in days:
if weekday == 1:
suffix = "st"
elif weekday == 2:
suffix = "nd"
elif weekday == 3:
suffix = "rd"
else:
suffix = "th"
print(day + " is the " + str(weekday) + suffix + " day of the week")
weekday = weekday + 1
Output 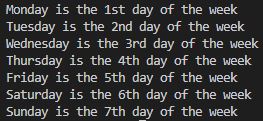
Programming for Animation Blog
| Status | In development |
| Category | Other |
| Author | up2115462 |
Leave a comment
Log in with itch.io to leave a comment.